OSBoxes – Virtual Machines for VirtualBox & VMware
UmairMoves a virtual machine stored in the VMM library or deployed on a host to a new location on a host. Move-SCVMHost: Moves a virtual machine host managed by VMM from one host group to another. Move-SCVMHostCluster: Moves a host cluster object managed by VMM from one host group to another. May 02, 2016 It is free to use, has an outstanding performance, excellent quality on the virtual machine, and the downloading process is really easy. Virtualization is very different from emulators. VirtualBox runs on your computer as a guest, so it thinks it is the host, but in reality, the code is not allowed to make any changes on the host, your PC. Mac OS X build instructions Prerequisites on Mac OS X 10.10.x (Yosemite) or later running on Intel hardware (PowerPC hardware is not supported nor is building an X11 variant). Download a virtual machine. We currently package our virtual machines for four different virtualization software options: VMWare, Hyper-V, VirtualBox, and Parallels. This VM will expire on 11/14/21. Windows 10, version 21H1 (10.0.19043) Windows 10 SDK, version 2104 (10.0.20348.0) Visual Studio 2019 (latest as of 8/19/21) with the UWP,.NET. VirtualBox is a general-purpose full virtualizer for x86 hardware, targeted at server, desktop and embedded use.For a thorough introduction to virtualization and VirtualBox.
Our other project has to offer you Tutorials/Reviews/Themes/Conky and much more for Ubuntu & derivatives.
Check out site for more options and information.
OSBoxes offers you ready-to-use Linux/Unix guest operating systems.

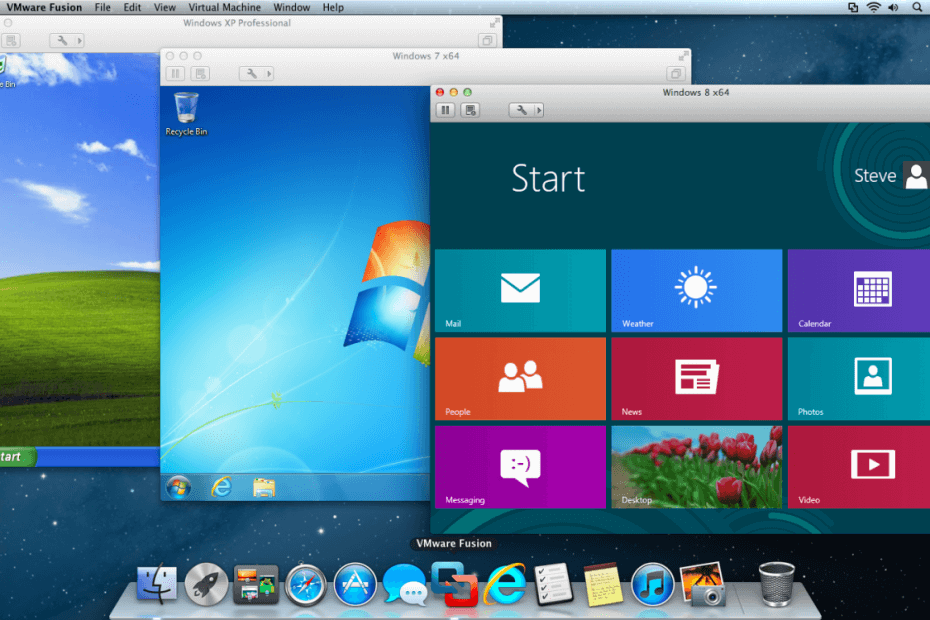
If you don’t want to install secondary OS alongside with your main OS but still want to use/try it, then you can use VirtualBox or VMware on your host operating system to run virtual machine.
VirtualBox
VMware
Latest Posts
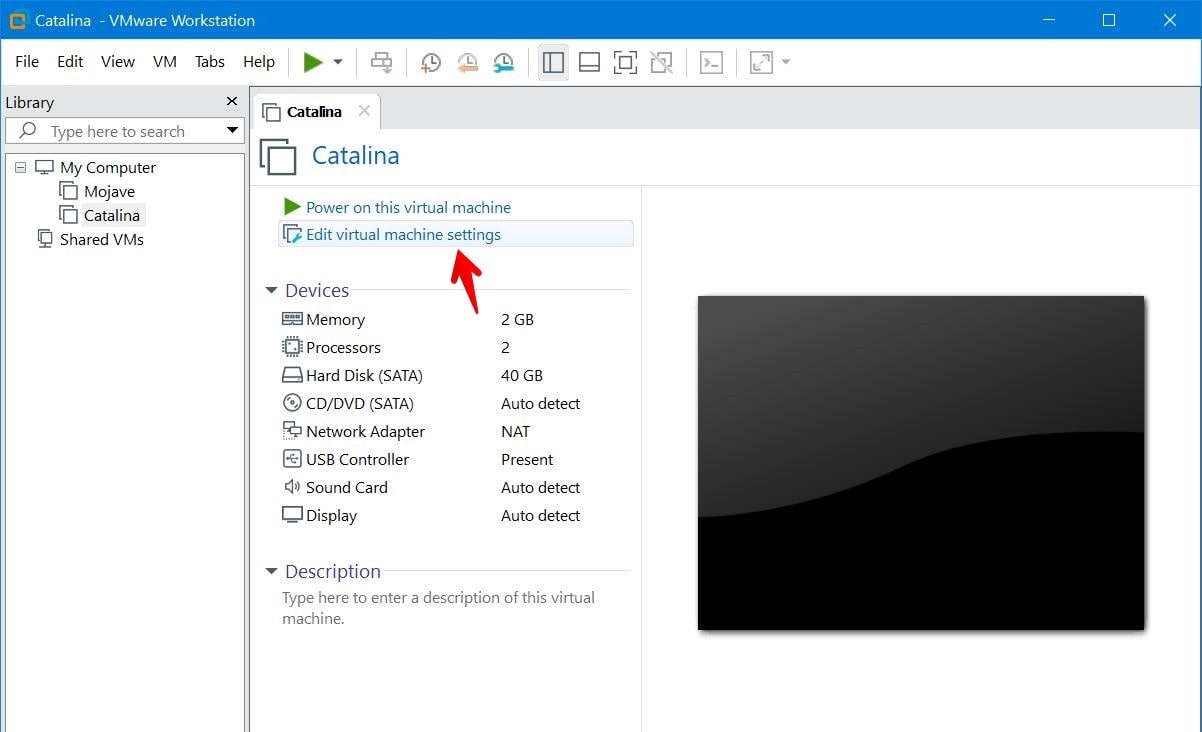
Contains:
- VMware virtual machine with guest operating system CentOS-6.4 64-bit minimal, plus:
- System libraries: gcc, kernel-devel, make, patch, vim-enhanced, httpd, openssh-clients, mod_ssl, wget, ntp, crontabs, perl, rcs, tcpdump, time, zip, unzip, gd
- Perl libraries: perl-CGI, perl-CGI-Session, perl-HTML-Parser, perl-Archive-Tar, perl-Authen-SASL, perl-GD, perl-libwww-perl
CentOS (Community Enterprise Operating System) is a very popular Linux distribution based on RedHat Enterprise Linux. The default CentOS distribution is too bloated for webserver use. This article describes how to build and use a VMware virtual machine containing a minimal CentOS-6.4 64-bit guest operating system, enhanced with libraries typically needed in a server environment. The VMware virtual machine image can be downloaded as well, which enables you to quickly and easily run Linux on Windows, Mac OS-X or any other x86 based platforms VMware and VirtualBox (Oracle VM) supports.
The TWiki project releases TWiki also as a VMware virtual machine (VM). Previous TWiki releases contained CentOS-5. The latest TWiki-VM-6.0.0-1 uses CentOS-6. There are CentOS-6 VMware images readily available for download, but they have a lot of bloat that is not needed in a server environment. There is a minimal distribution of CentOS-6 that has no GUI, it boots directly into a shell console. There was no VMware image with CentOS-6 minimal available for download, so we had to build one from scratch. We added the Apache webserver, cron, Perl and other libraries typically needed in a server environment. The result is a CentOS-6.4 64-bit distribution, packaged as a VMware image that can be readily used to run dynamic websites and other server applications.
Ho to use CentOS-6.4-64-bit-min-httpd:
- If you don't have VMware, install one of the VMware products from http://www.vmware.com/products/
- VMware offers free downloads for Windows platforms
- Download CentOS-6.4-64-bit-min-httpd.vmwarevm.zip
- We used this image as a base for the TWiki-VM-6.0.0-1 virtual machine. How about downloading the TWiki VM instead, and using it as a collaboration platform for your team?
- Copy the package to the directory where VMware keeps all images.
- Unzip the package, this creates a
CentOS-6.4-64-bit-min-httpd.vmwarevmdirectory with the image files.
A leading open source enterprise wiki and web application platform used by 50,000 small businesses, many Fortune 500 companies, and millions of people.
- Add the VM image to VMware:
- If you have a VMware ESX product you need to convert the VM image to the ESX format using the
vmkfstoolstool. Consult the VMware vmkfstools documentation - In the Virtual Machine Library of VMware, open the
.vmxfile located in theCentOS-6.4-64-bit-min-httpd.vmwarevmfolder - Boot the CentOS-6.4-64-bit-min-httpd image
- If you have a VMware ESX product you need to convert the VM image to the ESX format using the
- Change the root password:
- In the CentOS-6.4-64-bit-min-httpd.vmwarevm console screen, login as
rootwith passwordchangeme - At the prompt, type
passwdand enter a new (strong) password twice:# passwdChanging password for user root.New UNIX password:Retype new UNIX password:
- In the CentOS-6.4-64-bit-min-httpd.vmwarevm console screen, login as
- Set networking:
- The VM is configured for DHCP. This is OK for home use and for testing. In a production environment it should be changed to a static IP address.
- Network configuration for DHCP: Login as root, edit
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0and set its content to the following:DEVICE=eth0ONBOOT=yesBOOTPROTO=dhcp - Network configuration for static IP address: Login as root, edit
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0and set its content to the following: (tweak the IP address, net mask and gateway as needed)DEVICE=eth0ONBOOT=yesBOOTPROTO=noneTYPE=EthernetUSERCTL=noIPV6INIT=noPEERDNS=yesIPADDR=10.1.10.129NETMASK=255.255.255.0GATEWAY=10.1.10.1 - Restart the network after each configuration change: Login as root and enter this command:
# /etc/init.d/network restart 2- If you get this error:
Bringing up interface eth0: Device eth0 does not seem to be present, delaying initialization.
you have a MAC address mismatch. This can happen when you 'copy' (vs. 'move') a virtual machine the first time you start it. On copy, VMware assigns a new MAC address to the network interfaces, but may fail to update the Linux configuration files to mirror these changes, resulting in a dead eth0 network interface. - Fix:
- Edit
/etc/udev/rules.d/70-persistent-net.rules, delete the firstSUBSYSTEMsetting containingNAME='eth0', and change theNAMEin the secondSUBSYSTEMsetting from'eth1'toNAME='eth0'. Example:SUBSYSTEM'net', ACTION'add', DRIVERS'?*', ATTR{address}'00:0c:29:56:26:13', ATTR{type}'1', KERNEL'eth*', NAME='eth0' - Edit
/etc/sysconfig/networking/devices/ifcfg-eth0, remove also theUUIDsetting, and set theHWADDRsetting to the new MAC address. Example:HWADDR=00:0C:29:56:26:13 - Reboot the machine:
# reboot
- Edit
- If you get this error:
- Confirm (or find out) the IP address of the VM: Login as root and enter the
ifconfigcommand. In this sample output, look for theinet addrin the second line (ineth0section) :eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:0C:29:89:8C:47inet addr:192.168.1.79 Bcast:192.168.1.255 Mask:255.255.255.0inet6 addr: fe80::20c:29ff:fe89:8c47/64 Scope:LinkUP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1...
- Update CentOS and libraries with latest patches:
# yum update
- Configure the Domain Name System (DNS):
- Ask your IT to to add a DNS entry for your new server, such as
twiki.example.compointing to the IP address of the VM.
- Ask your IT to to add a DNS entry for your new server, such as
Step by step guide to build a CentOS-6.4 64-bit minimal VM with httpd and other libraries:
You can ignore this section if you simply want to use the CentOS virtual machine image. We used VMware Fusion 6.0 on Mac to build this virtual machine - the guide should also work for other VMware products.
- Starting at http://wiki.centos.org/Download, download
CentOS-6.4-x86_64-minimal.isoCD image from a mirror site- The CentOS-6.4-x86_64-minimal is a bare bone minimal CentOS without GUI.
- Create a CD from the .iso image - the image is just 360 MB so it fits easily on a CD.
- Note: Don't burn this as a single file to a CD, the .iso is the CD image. If burned properly you will see many files and directories in the CD.
- Create a new VMware image with CentOS:
- Open up the Virtual Machine Library of VMware
- Select menu: File => New... => More options... => Create custom virtual machine
- Select Linux OS => CentOS 64 bit
- Create a new virtual disk
- Name: CentOS-6.4-64-bit-min-httpd.vmwarevm
- Set root password: changeme (ignore the weak password warning)
- Once the image is created, boot CentOS-6.4-64-bit-min-httpd from the Virtual Machine Library
- Configure networking for DHCP and set host name:
- On the console, login as
rootwith passwordchangeme. # vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0:DEVICE=eth0TYPE=EthernetHWADDR=xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx(leave default)BOOTPROTO=dhcpNM_CONTROLLED=noONBOOT=yes# vi /etc/sysconfig/network:NETWORKING=yesNETWORKING_IPV6=noHOSTNAME=twiki# reboot# ping google.com# to verify proper networking
- On the console, login as
- Update OS:
# yum update# reboot
- Install VMware tools:
- In the Virtual Machine Library, select menu: Virtual Machine => Install VMware tools
- Install libraries:
# yum install gcc kernel-devel perl make openssh-clients httpd mod_ssl wget ntp crontabs vim-enhanced rcs tcpdump time patch zip unzip gd
- Configure httpd and crond to start on reboot:
# chkconfig httpd on# chkconfig crond on# chkconfig --list|egrep 'http|cron'should return:crond 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:offhttpd 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
- Disable Selinux:
# vi /etc/selinux/config:SELINUX=disabled
- Configure firewall to allow http:
# vi /etc/sysconfig/iptables:
beforeCOMMITadd this:-I RH-Firewall-1-INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT
- Restart network:
# /etc/init.d/network restart 2 - Install Perl libraries:
# yum install perl-CGI perl-CGI-Session perl-HTML-Parser perl-Archive-Tar perl-Authen-SASL perl-GD perl-libwww-perl - Power down VM:
# shutdown -h 0 - Open a terminal and change to the directory where VMware keeps the virtual machines.
- Delete
vmware*.logfiles in theCentOS-6.4-64-bit-min-httpd.vmwarevmdirectory. - Delete the
cachesdirectory in theCentOS-6.4-64-bit-min-httpd.vmwarevmdirectory if present. - Zip up the
CentOS-6.4-64-bit-min-httpd.vmwarevmdirectory asCentOS-6.4-64-bit-min-httpd.vmwarevm.zip
Congratulations, you just built a minimal CentOS-6.4 with apache & cron installed, ready for server use!
Windows 10 Iso File For Virtualbox
We used this image as a base for the TWiki-VM-6.0.0-1 virtual machine. How about downloading the TWiki VM and using it as a collaboration platform for your team?
Virtual Machine Library Mac Download Full
Let us know in the comments below how you built your virtual machine, and for what purposes.